The article “Cloud Computing Enabled Big Multi-Omics Data Analytics” by Koppad et al. explores the growing role of cloud computing in managing and analyzing complex multi-omics datasets. Multi-omics enables the development of a deeper and more fundamental understanding of the human being. However, the volume, complexity, and heterogeneity of these datasets present significant challenges in terms of storage, processing, and data integration. Traditional data analysis platforms struggle with computational demands and data integration across multiple omics layers.
Note: Multi-omics encompasses diverse biological data types—such as genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics.
Which is the role of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing provides scalable storage, high-performance computing resources, and flexible data management solutions. It supports distributed computing environments, facilitating data sharing and collaboration among researchers globally. Data can be accessed from anywhere. The pay-as-you-go model optimizes costs, enabling researchers to utilize powerful computational resources without heavy upfront investments.
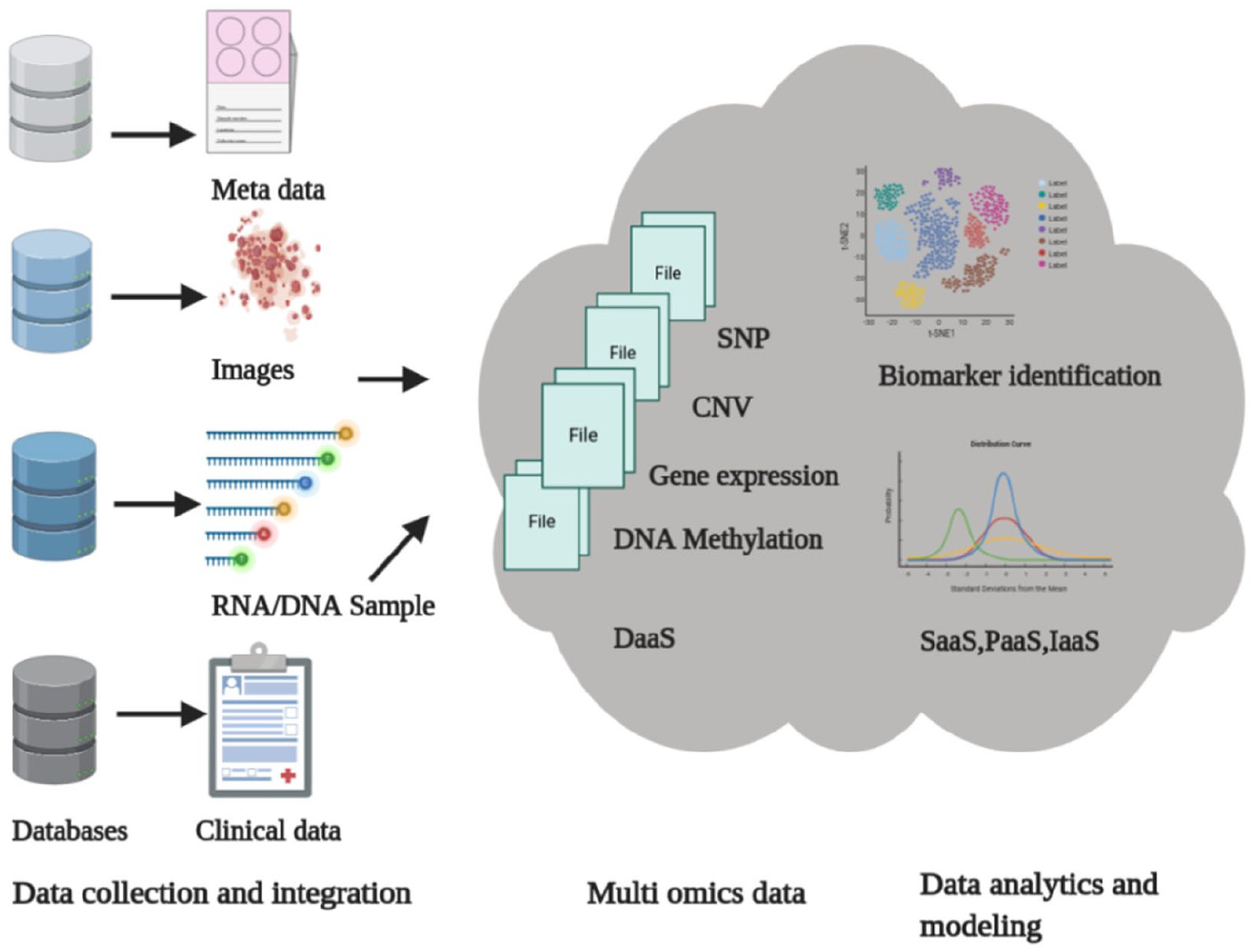
The study reviews state-of-the-art cloud-based technologies and big data analytics platforms, such as Apache Hadoop, Spark, and cloud-native bioinformatics tools. Emphasis is placed on using containerization (e.g., Docker) and workflow management systems (e.g., Nextflow) to ensure reproducibility and scalability in multi-omics data processing.
Discusses integrative analytics methods, including machine learning and network-based approaches, that enhance the interpretation of complex biological interactions. Cloud platforms support advanced visualization techniques, facilitating better data interpretation and hypothesis generation.
The authors conclude that cloud computing represents a transformative technology for multi-omics data analytics, promoting collaborative research and accelerating biological discoveries. They highlight the need for ongoing advancements in cloud infrastructure and analytics methodologies to fully harness the potential of big multi-omics data.